What is Alzheimer?
- Home
- What is Alzheimer?
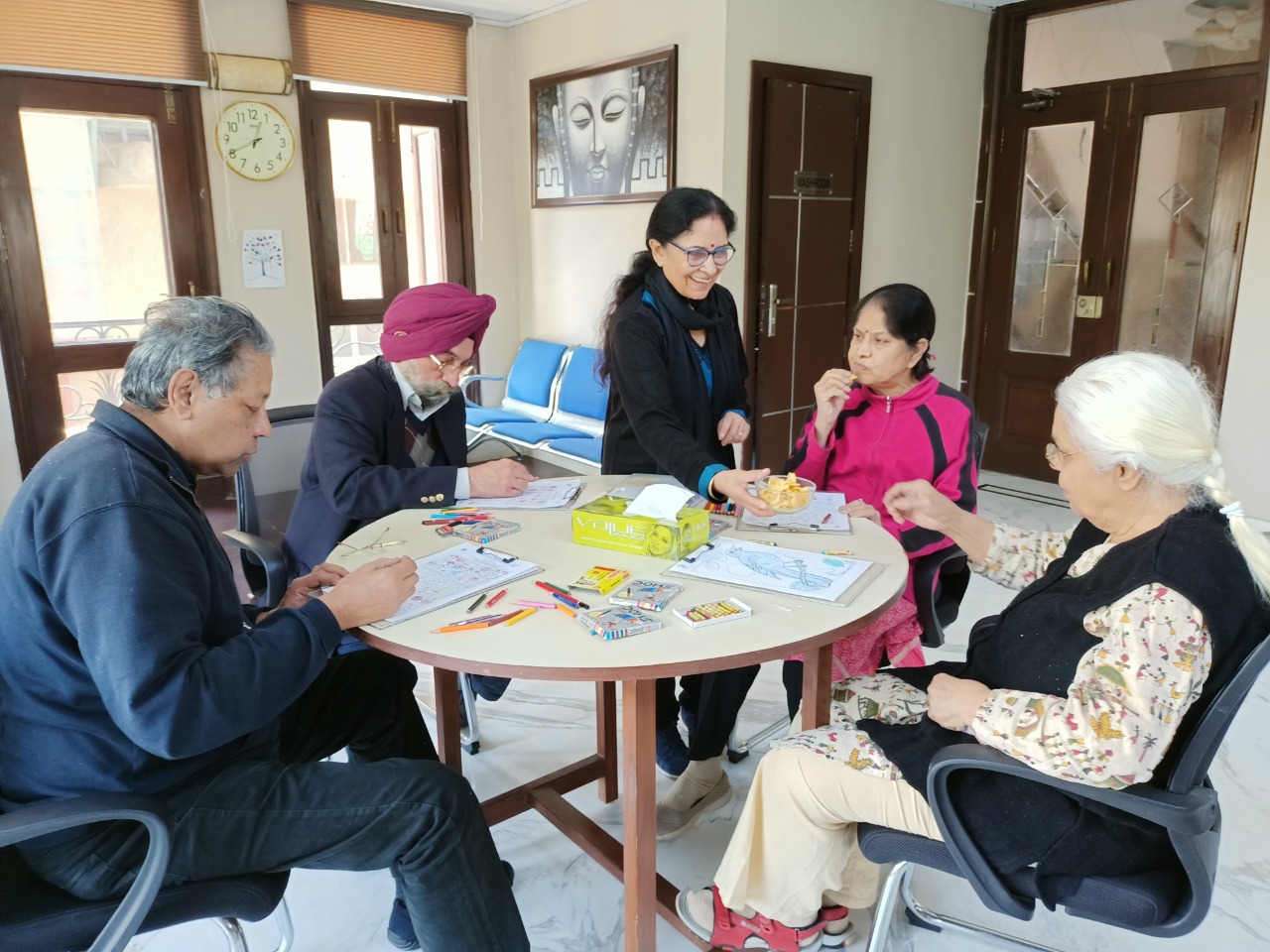
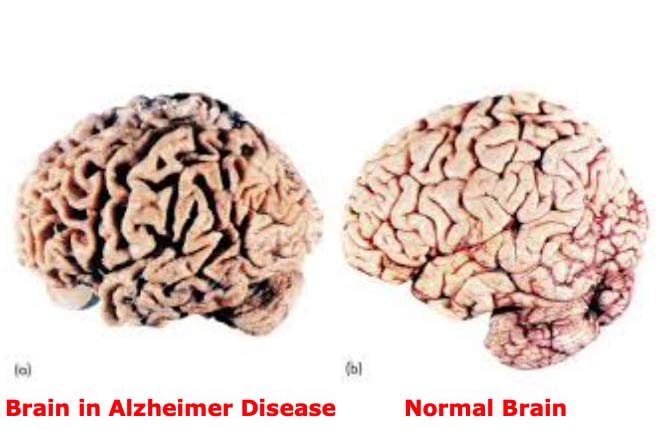
Dementia is a progressive illness of the brain. It is a disease or a medical condition that is characterised by a decline in memory, thinking skills, language and problem solving, which also affects a person's ability to perform everyday activities. Dementia causes brain cells to deteriorate more quickly than they normally do, which causes confusion about one's identity, where one is, and what day it is. The most typical form of dementia is Alzheimer's disease. Today, India is grappling with a surge in cases of dementia. The most unfortunate part is that dementia has no cure. Leading medical institutions around the world continue to conduct research and experiments, but finding a cure for dementia is still a difficult task for researchers and medical experts.
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive degenerative disorder of the Brain causing problems with memory, thinking and behaviour. It is the most common form of Dementia affecting around 3 million people in India and around 5 million people in USA. There is no cure for Alzheimer Disease till now but certain medicines can delay the progress. Death from the disease is actually due to secondary infection